Blog
What Is the Best Painkiller for Knee Pain?
Knee pain is a prevalent issue affecting people of all ages. Whether it’s due to an injury, arthritis, or overuse, finding effective pain relief is crucial for maintaining mobility and quality of life. This comprehensive guide explores the best painkiller for knee pain, including over-the-counter options, prescription medications, and alternative therapies.

Understanding Knee Pain
Common Causes of Knee Pain
- Osteoarthritis: Degeneration of cartilage leading to pain and stiffness.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: An autoimmune disorder causing joint inflammation.
- Injuries: Such as ligament tears, meniscus injuries, or fractures.
- Tendinitis: Inflammation of the tendons due to overuse.
- Bursitis: Inflammation of the fluid-filled sacs cushioning the knee joint.
Understanding the root cause of your knee pain is essential for choosing the most effective treatment.
Over-the-Counter Painkillers
Acetaminophen (Tylenol)
How It Works: Acetaminophen helps reduce pain by blocking pain signals in the brain but does not reduce inflammation.
When to Use: Suitable for mild to moderate knee pain without significant inflammation.
Dosage: Follow the recommended dosage on the label or as advised by a healthcare professional.
Pros:
- Fewer gastrointestinal side effects compared to NSAIDs.
- Safe for individuals who cannot take NSAIDs.
Cons:
- Overuse can lead to liver damage.
- Less effective for pain involving inflammation.
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
Common NSAIDs:
- Ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin)
- Naproxen (Aleve)
- Aspirin
How They Work: NSAIDs reduce inflammation by inhibiting enzymes (COX-1 and COX-2) involved in the inflammatory process.
When to Use: Effective for mild to moderate pain with associated inflammation.
Dosage: Use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration necessary.
Pros:
- Reduce both pain and inflammation.
- Widely available without a prescription.
Cons:
- May cause stomach irritation or ulcers.
- Not recommended for individuals with certain health conditions like kidney disease.
Prescription Medications
Stronger NSAIDs
Examples:
- Diclofenac
- Celecoxib (Celebrex)
When to Use: For moderate to severe pain not relieved by over-the-counter NSAIDs.
Pros:
- More potent anti-inflammatory effects.
- Targeted COX-2 inhibitors like Celecoxib may have fewer gastrointestinal side effects.
Cons:
- Require a prescription.
- Potential cardiovascular risks with long-term use.
Opioids
Examples:
- Tramadol
- Oxycodone
- Morphine
When to Use: Reserved for severe pain under strict medical supervision.
Pros:
- Highly effective for acute, severe pain.
Cons:
- Risk of addiction and dependency.
- Side effects include drowsiness, constipation, and nausea.
Topical Analgesics
Examples:
- Capsaicin Cream
- Diclofenac Gel (Voltaren Gel)
How They Work: Applied directly to the skin over the knee to reduce pain signals.
Pros:
- Fewer systemic side effects.
- Useful for localized pain relief.
Cons:
- May cause skin irritation.
- Variable effectiveness.
Corticosteroids
Administration: Injected directly into the knee joint.
When to Use: For severe inflammation and pain not responsive to other treatments.
Pros:
- Potent anti-inflammatory effects.
- Provides relief for weeks to months.
Cons:
- Invasive procedure.
- Potential side effects like joint infection or cartilage damage.

Alternative Therapies
Physical Therapy
Benefits:
- Strengthens muscles around the knee.
- Improves flexibility and range of motion.
Techniques:
- Exercise Programs
- Manual Therapy
- Ultrasound Therapy
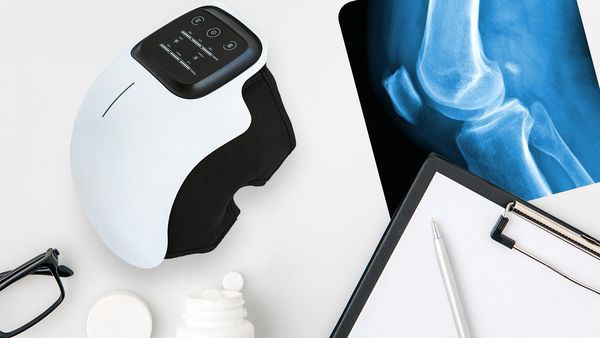
Knee Massagers
How They Work: Devices designed to provide heat, vibration, and compression therapy to alleviate knee pain.
Benefits:
- Improves Circulation: Enhances blood flow to promote healing.
- Reduces Stiffness: Heat and massage can loosen tight muscles.
- Convenient: Can be used at home without professional supervision.
For more information, you can visit the Monkika Knee Massager product page.
Supplements
Common Supplements:
- Glucosamine and Chondroitin
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids
- Turmeric (Curcumin)
Pros:
- May reduce inflammation and improve joint health.
- Generally safe with minimal side effects.
Cons:
- Variable scientific evidence regarding effectiveness.
- May interact with other medications.

Choosing the best Painkiller for knee pain
Factors to Consider
- Severity of Pain: Mild, moderate, or severe.
- Underlying Cause: Arthritis, injury, or overuse.
- Medical History: Existing health conditions and medications.
- Side Effects: Risk of gastrointestinal issues, cardiovascular risks, etc.
- Age: Older adults may have different risk profiles.
Consultation: Always consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
Safety and Side Effects
- NSAIDs: Risk of stomach ulcers, kidney damage, and increased blood pressure.
- Acetaminophen: Risk of liver damage with excessive use.
- Opioids: Risk of addiction, respiratory depression, and overdose.
- Corticosteroids: Potential joint damage with repeated injections.
General Tips:
- Follow Dosage Instructions: Do not exceed recommended amounts.
- Avoid Mixing Medications: Unless advised by a healthcare provider.
- Monitor for Allergic Reactions: Seek immediate help if symptoms occur.
Conclusion
Finding the best painkiller for knee pain depends on various factors, including the cause and severity of your pain, as well as your overall health. Over-the-counter options like acetaminophen and NSAIDs are effective for many people, but prescription medications and alternative therapies may be necessary for others.
For those interested in non-pharmacological options, therapies like physical therapy and knee massagers can offer significant relief. Devices such as the Monkika Knee Massager provide convenient, at-home solutions that complement traditional treatments.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult your healthcare provider before starting any new treatment.
This is an advertisement and not an actual news article, blog, or consumer protection update the story depicted on this site and the person depicted in the story are not actual news. Rather, this story is based on the results that some people who have used these products have achieved. The results portrayed in the story and in the comments are illustrative, and may not be the results that you achieve with these products. this page could receive compensation for clicks on or purchase of products featured on this site.
© 2024 All Rights Reserved. Privacy Policy – Terms of Service




